General
- Essentially a large group of disorders that affect the alveolar wall that potentially leads to diffuse scarring and fibrosis
- Traditionally termed Interstitial Lung Disease however its a misnomer
- The interstitium formally refers only to the region of the alveolar wall exclusive of and separating the alveolar epithelial cells and capillary endothelial cells
- But interstitial lung diseases affect all components of the alveolar wall: epithelial cell, endothelial cell, and cellular and noncellular components of the interstitium
- usually extends into the alveolar spaces so now its called diffuse parenchymal lung disease
- Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias
- a group of pathologic entities that represent a subcategory of DPLD
Pathology
- Two major pathologic components that occur simultaneously
- inflammatory process in the alveolar wall and alveolar spaces (sometimes called alveolitis)
- scarring or fibrotic process
- Active inflammation is the primary process and fibrosis that follows is a secondary feature
- Exception: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in which the primary process is epithelial cell injury and fibrosis representing an abnormal repair of injury rather than alveolar inflammation
- Active alveolitis
- Presence of a variety of inflammatory cells (macrophages, lymphocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, and plasma cells) that infiltrate the alveolar wall
- Types of DPLD may be a/w a prominence of a specific inflammatory cell type (e.g. eosinophils in Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia)
- In addition to the presence of these inflammatory cells, other pathologic characteristics are useful in the diagnosis of a specific pathologic entity
- For example: Granuloma
- Granuloma typically also has multinucleated giant cells which result from the fusion of several phagocytic cells into a single large cell with abundant cytoplasm and many nuclei
- Usually reflects an underlying immune process or reaction to a specific agent
- DPLD with Granulomas = Sarcoidosis & Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
- Both have noncaseating granulomas
- For example: Granuloma
Pathology of Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias
- The term idiopathic indicates that a specific etiologic agent has not been identified for these disorders but we now know that smoking plays a contributory role or adds to the risk of developing several of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonia
- The terms used to describe the pathology and the associated clinical disorder may be different
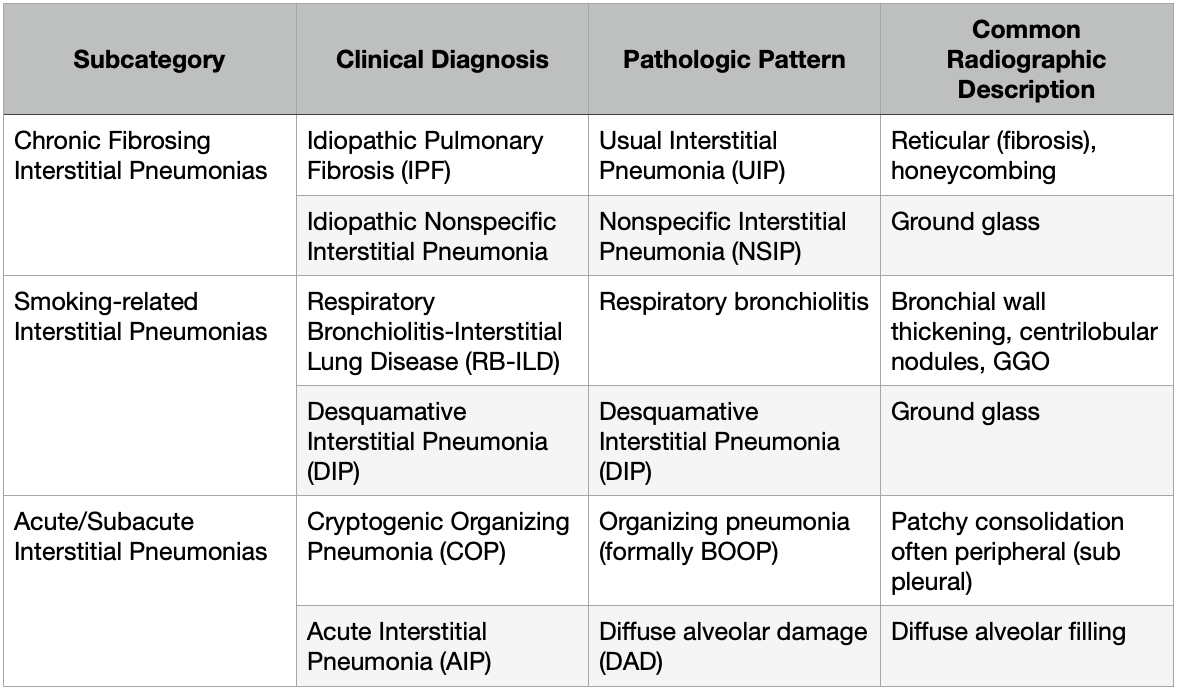
- Some of the pathologic patterns can be seen in lung disease a/w Connective Tissue Disease-Associated ILD
- For example: NSIP (the pathologic pattern) when not idiopathic, can be a particularly common pathologic expression of pulmonary involvement in diseases such as Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Systemic Sclerosis
-
Pathology of Acute Lung Injury
-
Pathology of Chronic Fibrosing Interstitial Pneumonias
-
Pathology of Smoking Related Interstitial Pneumonias
- Respiratory Bronchiolitis
-
- clinical features of interstitial lung disease = Respiratory Bronchiolitis-Associated ILD
-
- clinical features + fibrosis = Respiratory Bronchiolitis with Fibrosis
-
- Desquamative Interstitial Pneumonia
- Respiratory Bronchiolitis + clinical features of ILD + diffuse intrapulmonary spread
- Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
- Respiratory Bronchiolitis